Coenzyme Q10 (ubiquinone) is an ingredient found in lots of skincare products. Here’s the lowdown on what it is, and what it does for your skin.
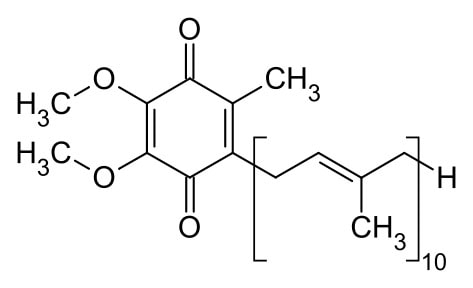
What Is Coenzyme Q10?
Coenzyme Q10 (also known as ubiquinone or CoQ10) is a fat-soluble substance found in almost every tissue in your body. Your body naturally produces a lot of it.
Its main roles are:
As an antioxidant: Coenzyme Q10 can go around mopping up reactive free radicals before they muck up your cells. Free radicals are generated in normal cell processes and by environmental stressors (UV, pollution), and when they react with parts of your body they’re not meant to, the damage can accumulate and show up as signs of aging.
Related post: Antioxidants in Skincare: What Do They Do?
In aerobic cellular respiration: Coenzyme Q10 is vital in aerobic energy production within the mitochrondria of your cells. Your body produces around 95% of its energy this way. “Aerobic” in this context doesn’t just mean walking and exercising, but all of the microscopic oxygen-consuming processes that go on inside your body that you don’t notice.
Coenzyme Q10 was discovered in 1957 and since then, its use has been researched extensively in the areas of cancer and heart disease.
What Does Coenzyme Q10 Do in Skincare?
It’s important in the body, but what happens when coenzyme Q10 is applied to your skin?
Antioxidant Activity and Sun Protection
Coenzyme Q10’s been mainly found to act as an antioxidant. It’s believed to be involved in preventing both chronological aging (loss of firmness in skin as you get older) and photoaging (wrinkling and drying of skin from excessive sun exposure). Applying coenzyme Q10 on the skin was found to increase antioxidant levels and decrease free radicals in a clinical trial.
It’s also expected that, like other antioxidants, coenzyme Q10 could help prevent the inflammation and wrinkling caused by the radicals formed in your skin after sun exposure. Cultured human skin cells treated with coenzyme Q10 suffered less damage when exposed to UVA and UVB light, and coenzyme Q10 prevented UVA-induced antioxidant decrease in elderly people’s skin.
Treating Wrinkles
As you get older, the levels of coenzyme Q10 in your body decreases, with peak levels occurring in your early 20s. It also decreases when you’re stressed or sick. It’s thought that this could lead to sagging skin, wrinkles and loss of firmness and elasticity.
So logically, you could potentially undo this by supplementing your skin with a coenzyme Q10-containing skincare product. And like most other antioxidants, it looks like it mostly acts on the upper layers (epidermis) rather than the deeper layers (dermis), with 10 times as much coenzyme Q10 found in the epidermis.
There aren’t many studies on topical coenzyme Q10 and aging skin, but a couple of trials found that topical 1% and 0.3% coenzyme Q10 cream reduced wrinkles. However, both of these studies were performed over a long period (5-6 months), so coenzyme Q10 may not be ideal for quick results.
Dietary Supplements
Taking coenzyme Q10 dietary supplements can also improve wrinkles and skin smoothness. It’s also found naturally in lots of different foods like meat, eggs, nuts and green vegetables.
Pigmentation
There’s also some evidence that coenzyme Q10 could work as a brightening agent, although so far the studies have been on cell lines and in zebrafish.
References
Chiu A, Kimball AB, Topical vitamins, minerals and botanical ingredients as modulators of environmental and chronological skin damage, Br J Dermatol 2003, 149, 681. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2133.2003.05540.x
Knott A et al., Topical treatment with coenzyme Q10-containing formulas improves skin’s Q10 level and provides antioxidative effects (open access), Biofactors 2015, 41, 383-90. DOI: 10.1002/biof.1239
Inui M et al., Mechanisms of inhibitory effects of CoQ10 on UVB-induced wrinkle formation in vitro and in vivo, Biofactors 2008, 32, 237-43. DOI: 10.1002/biof.5520320128
Hoppe U et al., Coenzyme Q10, a cutaneous antioxidant and energizer, Biofactors 1999, 9, 371-8. DOI: 10.1002/biof.5520320128
Žmitek K et al., The effect of dietary intake of coenzyme Q10 on skin parameters and condition: Results of a randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind study, Biofactors 2017, 43, 132-140. DOI: 10.1002/biof.1316
Hseu YC et al., The in vitro and in vivo depigmenting activity of Coenzyme Q10 through the down-regulation of α-MSH signaling pathways and induction of Nrf2/ARE-mediated antioxidant genes in UVA-irradiated skin keratinocytes, Biochem Pharmacol 2019, 164, 299-310. DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2019.04.015
[lastupdated]





i really like your blog..have fun reading it
Thank you 🙂
love your blog… i’ve even bought some of the products you’ve showcased and been amazed by them!
Thanks! 🙂 I’m always worried about my rave reviews, in case something works for me and no one else, so I’m really glad they worked for you too!
Great read! Thanks for informing me on something new ^-^
Hello and thank you for the explanation. Is ubiquinone really the same as coenzyme Q? Also… would you please provide us with the newest studies on the anti ageing effect of Coenzymy Q?
Furthermore, do I understand correctly, that Coenzyme Q is able to get into the dermis level?
Thank you!
Very interesting blog, the information is very useful
I didn’t realize this was written a long time ago, but I still found it very informative. Very easy to understand as well. Thank you for sharing it to the world!
Great explanation, easy to understand! I’ve noticed glutathione in a lot of skincare products. Does it work in a similar fashion as Coenzyme Q10 does?
Very informative. Thank you.
I’d love to see the before and after pictures of the zebra fish 🙂